What is Solar Energy and How Does it Work?
Solar energy is a powerful and growing source of renewable energy. It utilizes sunlight to generate electricity and heat. According to Dr. Maria Jensen, a leading expert about solar energy, “Harnessing the sun’s power can change our energy landscape.” Her statement reflects the transformative potential of solar energy technologies.
In recent years, solar panels have become more efficient and accessible. Many households are now integrating solar solutions into their energy consumption. Cities are also investing in solar farms and infrastructure. This shift highlights a collective move towards sustainability. However, challenges remain in terms of storage and off-grid solutions.
Despite the push for solar energy, questions arise. Are we maximizing its potential? Can we overcome the obstacles of cost and adoption? These difficulties urge us to reflect on our strategies. Truly harnessing solar energy requires innovation and community support to create lasting change.

What is Solar Energy?
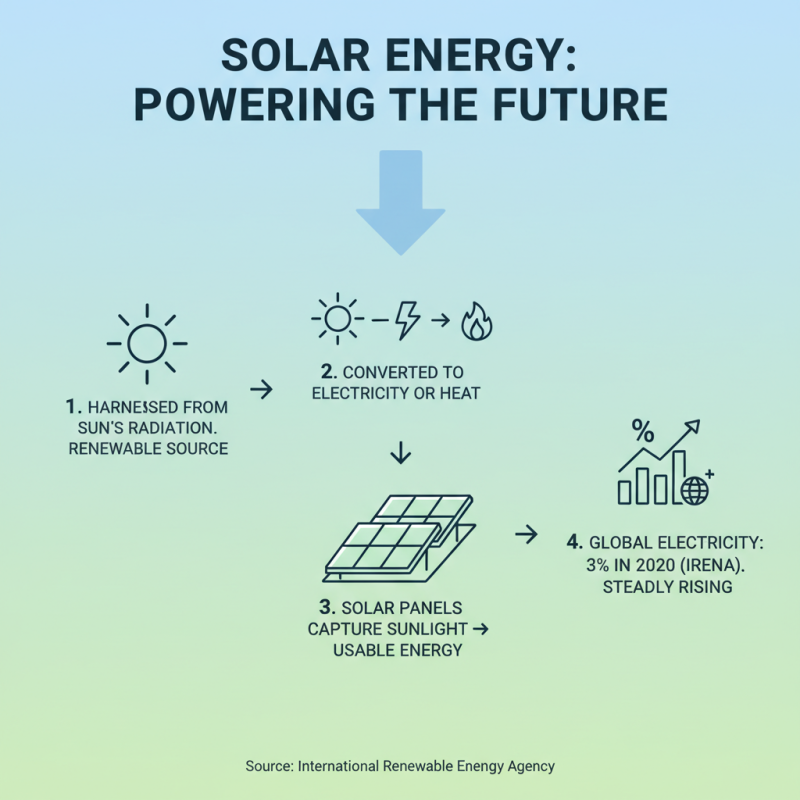
Solar energy is harnessed from the sun's radiation. It is a renewable source of power. This energy is converted into electricity or heat. Solar panels capture sunlight and transform it into usable energy. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, solar energy accounted for 3% of global electricity generation in 2020. This number is steadily rising.
Not all places benefit equally from solar energy. Geographic location plays a significant role. Regions with high sunlight exposure see more efficiency. However, areas with frequent cloud cover struggle to maximize solar technology's potential. A report by the International Energy Agency states that solar installations could reach 1,200 gigawatts by 2022. Still, there are concerns about sustainability.
Solar technology requires significant resources for panel production. This process can lead to environmental degradation if not managed responsibly. End-of-life disposal of solar panels presents challenges too. Awareness and reflection on these issues are crucial for future advancements. As solar energy grows, addressing these complexities is key.
Types of Solar Energy Technologies
Solar energy is a rapidly growing field with various technologies harnessing sunlight.
Photovoltaic (PV) cells are the most common type. They convert sunlight directly into electricity. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global solar capacity reached around 760 gigawatts in 2020. This impressive figure is indicative of increased adoption, but challenges remain. The efficiency of PV cells still averages about 15-20%, leaving room for improvement.
Concentrated solar power (CSP) is another technology worth noting. CSP systems use mirrors to focus sunlight. This focused light generates heat, which produces electricity through steam turbines. Reports suggest that CSP accounted for about 14% of the total solar energy generation in 2020. This technology, however, requires significant land and water resources. This raises concerns in arid regions where water scarcity is a critical issue.
Solar thermal technology harnesses sunlight for heating applications. It is widely used for water heating in residential and commercial settings. The effectiveness of solar thermal systems can vary greatly depending on location and weather patterns. Some regions may not receive consistent sunlight throughout the year. These factors influence the overall performance and reliability of solar thermal installations. The path forward for solar technologies is promising, yet it demands ongoing innovation and adaptation to overcome existing hurdles.
How Solar Panels Convert Sunlight into Electricity
Solar energy is a powerful renewable resource. It harnesses sunlight to generate electricity, primarily through solar panels. These panels are made of photovoltaic cells that absorb sunlight. When sunlight hits these cells, it generates direct current (DC) electricity.
This DC electricity must be converted into alternating current (AC) to power homes and businesses. An inverter conducts this conversion. After that, the electricity flows into the electrical panel, ready for use. It might seem complex, but the process is quite efficient. Some panels can produce energy even on cloudy days.
Tips: Consider your roof angle and location. These factors affect panel efficiency. Maintenance is also vital. Clean panels can absorb more sunlight. Regular checks ensure they work well. Even with optimal conditions, some energy may be lost. Reflect on ways to improve your system's efficiency. Utilize battery storage to maximize your solar energy use.
The Benefits of Utilizing Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses the sun's power, providing a clean, renewable energy source. Utilizing solar panels, sunlight is converted into electricity. This method reduces reliance on fossil fuels, leading to a significant decrease in greenhouse gases. The sunshine is abundant and free, making it an attractive option for energy generation. Homes and businesses can benefit from this technology, lowering electricity bills.
One major advantage of solar energy is its sustainability. Unlike traditional energy sources, the sun won't deplete. However, solar energy production is not perfect. Cloudy days do hinder efficiency. Despite that, advancements continue to improve technology. Furthermore, solar energy installations can require substantial initial investments. This can be a barrier for many.
The potential for job creation in the solar industry is notable. Innovation can lead to diverse roles, from manufacturing to installation. However, workforce training remains a pressing concern. Sometimes, communities lack the necessary resources for training. Nonetheless, embracing solar energy can lead to a cleaner, brighter future for everyone.
Solar Energy Usage by Sector in 2023
This chart represents the distribution of solar energy utilization across different sectors in 2023. As more organizations and households adopt solar technology, the share of energy sourced from solar power continues to grow.
The Future of Solar Energy and Its Impact on the Environment
The future of solar energy looks promising, with potential benefits for the environment. According to the International Energy Agency, solar power could supply 20% of global electricity by 2040. This shift would significantly reduce carbon emissions. Currently, about 1.2 billion tons of carbon dioxide can be avoided annually, thanks to solar solutions.
Investing in solar technology has its challenges. The initial costs can be high. However, advancements in technology and government incentives are helping lower these barriers. In the U.S., solar jobs increased by 167% between 2010 and 2020, according to the Solar Foundation. This growth contributes to reducing unemployment and boosting local economies.
Tips: Consider installing solar panels if you have the resources. Monitor energy consumption to maximize savings. Community solar programs are also worth exploring. They can make solar energy accessible without the upfront costs. Remember, while solar energy offers great promise, not all areas receive equal sunlight. Evaluate your options carefully before committing.
What is Solar Energy and How Does it Work? - The Future of Solar Energy and Its Impact on the Environment
| Dimension | Description | Current Data | Future Projections |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Solar Capacity (2023) | Total installed solar energy capacity worldwide | 1,000 GW | 3,000 GW by 2030 |
| Solar Energy Share in Electricity Generation | Percentage of electricity generated from solar energy | 10% | 25% by 2030 |
| CO2 Emissions Reduction (2023) | Estimated CO2 emissions reduced due to solar energy usage | 1.5 billion metric tons | 4 billion metric tons by 2030 |
| Job Creation in Solar Industry | Number of jobs supported by the solar industry | 3 million jobs | 8 million jobs by 2030 |
| Cost of Solar Energy (Levelized Cost) | Average cost to produce a unit of solar energy | $30 per MWh | $20 per MWh by 2030 |
